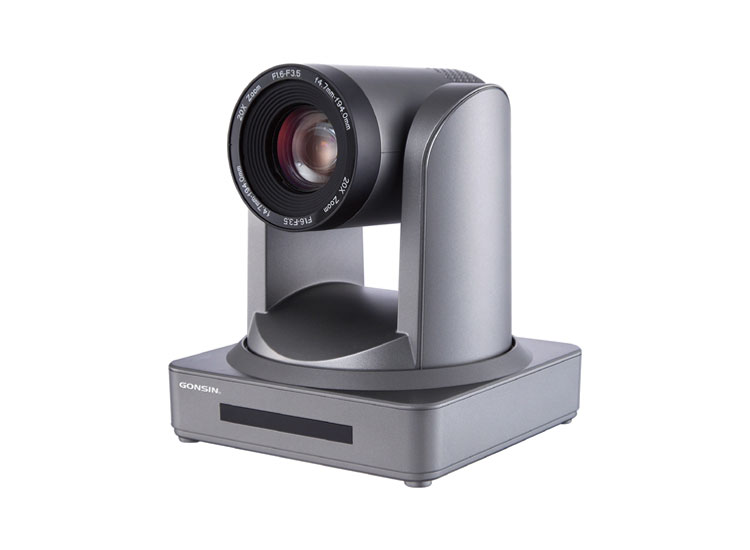
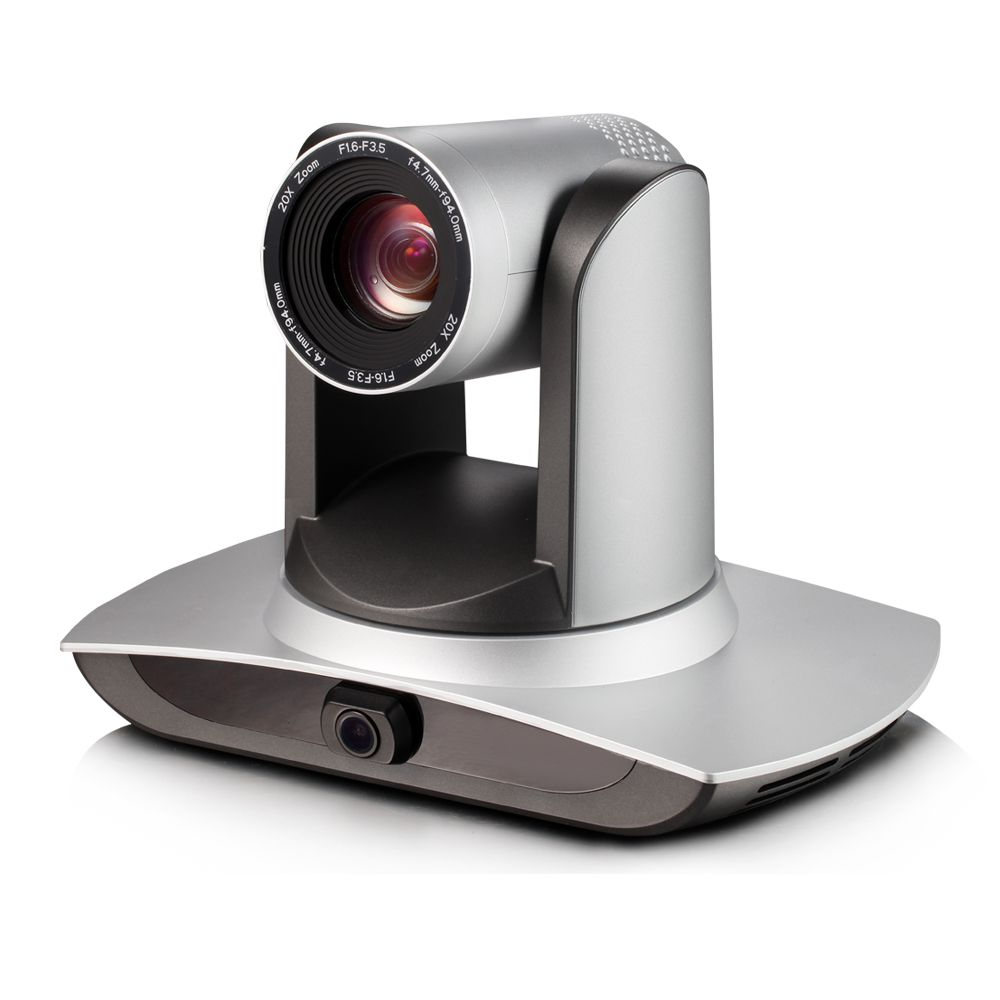
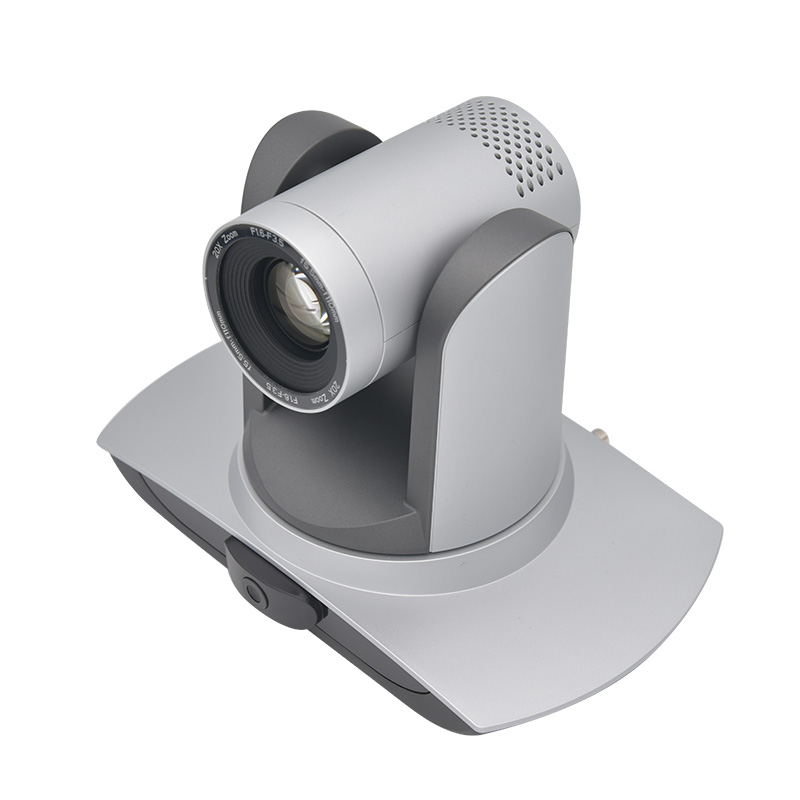
Camera tracking, also known as motion tracking, plays a pivotal role in various fields, from film production to security surveillance. It refers to the process of recording and analyzing the movement of cameras or objects within the footage captured by a camera.
Understanding the Essence of Camera Tracking
Camera tracking, fundamentally, is a process that captures and analyzes the movement of a camera through space or the movement of objects within the camera’s field of view. It is an essential tool in the creation of visual effects and in enhancing various forms of media and technology with realistic or interactive elements.
The Significance of Motion in Visual Media
At the heart of camera tracking lies the principle of motion. In visual media, the illusion of motion is what brings a scene to life, whether it’s through the graceful arc of a soaring superhero or the detailed environment that surrounds a video game character. Camera tracking allows creators to construct these dynamic narratives by ensuring that the movement within the virtual world aligns with movements in the real world.
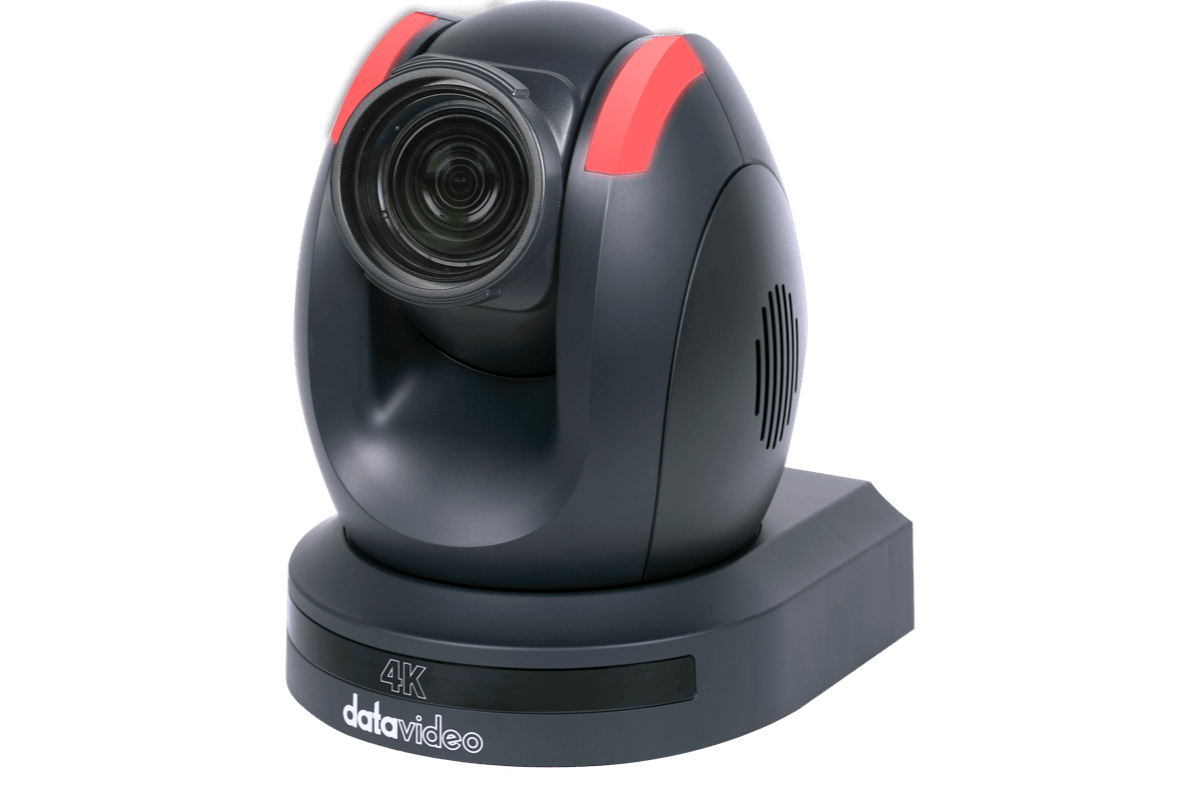

Technical Aspects of Camera Tracking
Technically, camera tracking involves recording the positional and rotational data of a camera over time. This data can then be used to recreate the same camera movements in a digital environment, allowing virtual and real elements to be composited together with spatial accuracy. High precision in camera tracking is crucial as it ensures that the virtual elements maintain the correct size, perspective, and position relative to the physical environment, even as the camera moves.
Types of Camera Tracking
There are two primary forms of camera tracking: matchmoving and motion capture. Matchmoving, also known as motion tracking, refers to the technique of matching CGI elements to live-action footage. Motion capture, on the other hand, is focused on capturing the movement of actors or objects to animate digital characters and elements realistically.
Integration of CG and Live Action
The integration of computer-generated (CG) imagery with live-action footage is one of the most magical capabilities granted by camera tracking. Visual effects artists use the data from camera tracking to ensure that the virtual elements behave as if they are part of the physical set, obeying the same lighting and physical laws. The result is a seamless blend between the real and the imagined, which is vital for maintaining the suspension of disbelief in movies and television.
Applications Beyond Entertainment
While camera tracking is most often associated with the entertainment industry, its applications extend far beyond. In the field of augmented reality (AR), for example, camera tracking allows digital overlays to interact with the real world in real-time, enhancing experiences in education, navigation, and commerce. In robotics and drone navigation, camera tracking helps machines understand their environment and move through it autonomously.
The Importance of Precision and Accuracy
The success of camera tracking rests on the precision and accuracy of the tracking data. Inaccurate tracking can result in visual artifacts, such as sliding or popping, which can disrupt the realism of a scene. As such, visual effects artists and technologists constantly refine their methods to achieve more accurate tracking, often employing sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques.
Enhancing Surveillance with Advanced Camera Tracking
Security camera tracking systems, also known as PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras, are designed to automatically follow moving objects or people across their field of view. This active monitoring capability is a significant step up from traditional fixed cameras, which only capture a static image of their direct line of sight.
The Dynamics of PTZ Cameras
PTZ cameras can swivel left or right (pan), move up or down (tilt), and zoom in on objects of interest. They can be programmed to move on pre-set guard tours or can be manually controlled by security personnel. The range of motion and zoom capabilities enable surveillance over expansive areas with the flexibility to focus on specific events as they unfold, providing a comprehensive security solution.
Automated Motion Detection and Following
One of the most sophisticated features of modern security camera tracking is the ability to detect and follow motion autonomously. Using advanced algorithms, these cameras can identify moving objects, lock onto them, and track their progress across the camera’s range. This ensures continuous monitoring and recording of potential security threats without the need for constant human intervention.
The Transformative Impact of Software on Camera Tracking
With the advent of sophisticated software, camera tracking has transcended the limitations of manual operation, allowing for real-time analysis and enhanced interaction with the recorded content. This technology has become crucial in extracting meaningful information from raw footage, whether that be for creating immersive worlds in film or monitoring secure locations.
Real-time Analysis and Response
In security applications, software enables cameras to analyze footage instantaneously, identify threats, and trigger alerts. This immediate processing allows for quick decision-making and can be the difference between a neutralized threat and a security breach.
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency
Advanced software algorithms improve the accuracy of camera tracking, reducing false positives and focusing on relevant movements. This not only saves time but also increases the overall efficiency of surveillance operations.
The Functionality of Video Analytics
Video analytics software can be considered the brain behind camera tracking systems. It interprets the visual data captured by cameras, providing insights that were previously unattainable through human observation alone.
Motion Detection and Pattern Recognition
Modern video analytics can discern patterns in movement and differentiate between various objects. This ability allows cameras to track people, vehicles, and other items, understanding context and relevance to a given situation.
Behavioral Analysis
Beyond simple motion tracking, some software can analyze behavior. And identifying actions that may indicate a security risk or other noteworthy events. It can alert personnel to unusual patterns, such as loitering or erratic movement, which could signify a potential threat.
Integration with Other Technologies
Camera tracking software doesn’t operate in isolation. It often works in conjunction with other systems and technologies to provide a more comprehensive solution.
Future Directions and Ethical Considerations
As software and analytics continue to evolve, they will offer even more sophisticated capabilities in camera tracking. However, this progress comes with ethical considerations, particularly regarding privacy and consent.
Future Developments in Security Camera Tracking
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are set to further revolutionize camera tracking in security. AI-driven cameras can learn from the environments they monitor, improving their ability to identify and track objects over time. They can also integrate with broader smart city infrastructure, enhancing public safety on a larger scale.